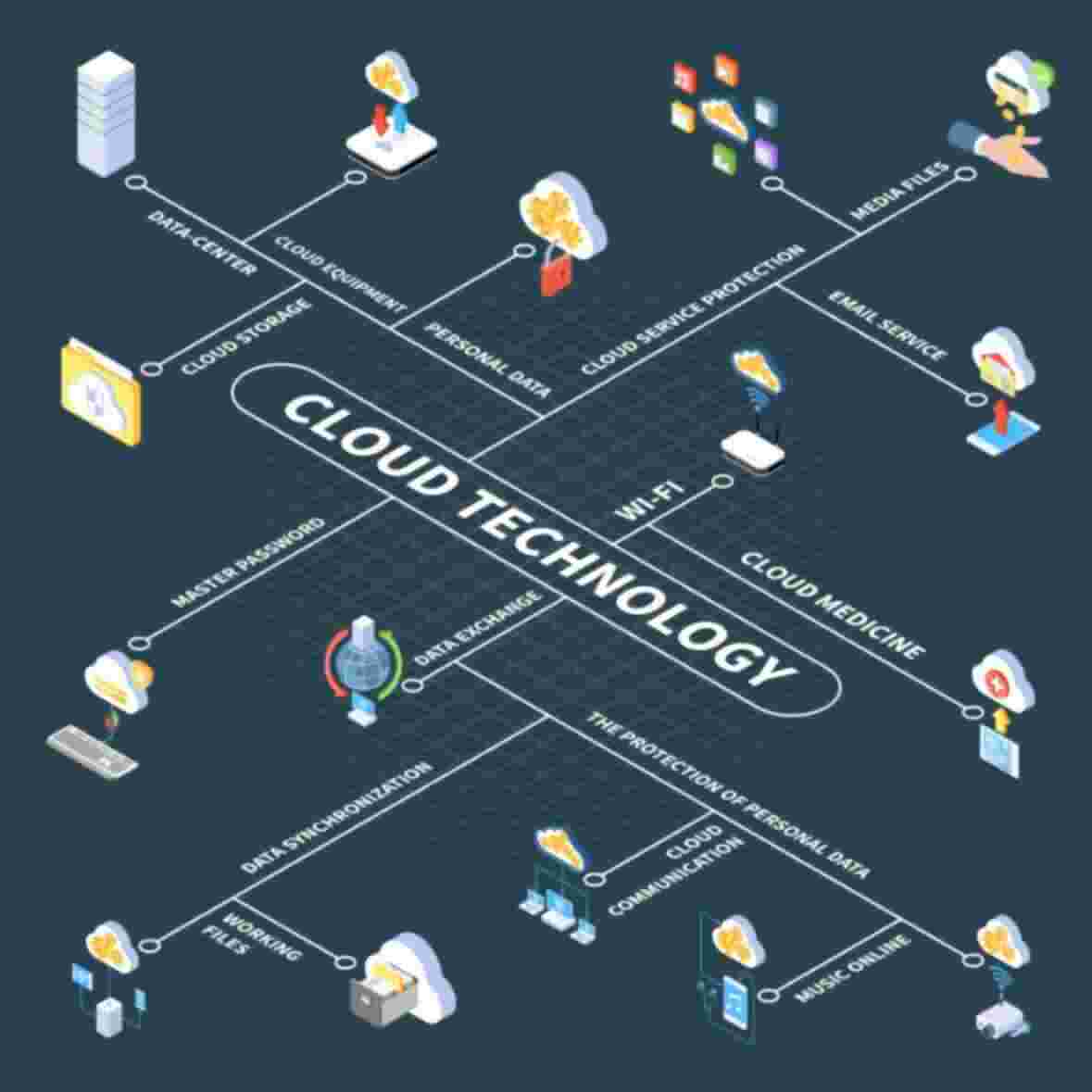
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to the cloud to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and improve their overall agility. Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern business, and within this realm, multi-cloud services have emerged as a strategic approach to meet diverse IT needs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of multi-cloud services, exploring what they are, providing real-world examples, discussing the three primary types of cloud-associated services, and unraveling the intricacies of multi-cloud infrastructure. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of the multi-cloud paradigm and how it can benefit your organization.
What are Multi-Cloud Services?
Multi-cloud services refer to the strategic use of multiple cloud providers and their services to address an organization’s specific IT requirements. In essence, it involves the orchestration and management of cloud resources across various cloud platforms. This approach is distinct from a single-cloud strategy, which relies on a sole cloud provider for all computing needs. Multi-cloud services provide several advantages, including improved redundancy, enhanced flexibility, and cost optimization.
Examples of Multi-Cloud
To illustrate the concept of multi-cloud services, let’s consider some real-world examples:
1. E-Commerce Platform: A global e-commerce platform may use Amazon Web Services (AWS) for its data warehousing needs, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for machine learning and analytics, and Microsoft Azure for its customer relationship management (CRM) system. By leveraging these diverse cloud providers, the company can ensure high availability and geographic redundancy, which is crucial for delivering a seamless shopping experience to customers worldwide.
2. Healthcare Organization: A healthcare provider may choose to host sensitive patient data on a private cloud while using a public cloud like AWS or Azure for non-sensitive applications. This ensures that confidential patient information is protected, while the organization can still capitalize on the public cloud’s scalability for less critical services.
The Three Types of Cloud-Associated Services
In the realm of multi-cloud services, it’s essential to understand the three primary types of cloud-associated services:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) delivers virtualized computing resources via the Internet, allowing organizations to lease servers, storage, and networking components from cloud providers. Prominent IaaS offerings, such as AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine, underscore the remarkable versatility of this service, a pivotal factor fueling its widespread adoption in multi-cloud environments.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a comprehensive platform for application development and deployment. With PaaS, businesses can focus on creating and running applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS, or Software as a Service, seamlessly delivers software applications via the internet, thereby obviating the necessity for users to install and manage software on their own devices. Prominent SaaS applications, such as Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce, demonstrate this model. Furthermore, the integration of multiple SaaS solutions from various providers plays an integral role in a well-rounded multi-cloud strategy.
Understanding Multi-Cloud Infrastructure
Multi-cloud infrastructure is the backbone of a multi-cloud strategy. It involves designing a network architecture that seamlessly connects multiple cloud environments, allowing data and applications to move between them efficiently. This infrastructure is characterized by the use of public, private, and hybrid clouds, orchestrated to meet specific business objectives.
Public clouds, such as AWS, GCP, and Azure, provide scalability and flexibility for workloads with varying demands. They are ideal for applications with fluctuating resource requirements.
Private clouds offer dedicated resources and enhanced security for mission-critical applications and sensitive data. Healthcare and finance industries, for instance, often rely on private clouds for compliance and data protection reasons.
Hybrid clouds bridge the gap between public and private clouds, allowing organizations to harness the benefits of both. They provide the agility of public clouds and the control of private clouds. Hybrid cloud architecture is particularly beneficial for businesses seeking to optimize resource allocation while maintaining data security.
Challenges and Benefits of Multi-Cloud Services
Implementing a multi-cloud strategy offers numerous benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these aspects is crucial for organizations considering this approach.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Services:
- Enhanced Redundancy: Multi-cloud services reduce the risk of downtime. If one cloud provider experiences an outage, your services can seamlessly shift to another provider, ensuring continuity of operations.
- Cost Optimization: Organizations can optimize costs by selecting the most cost-effective cloud service for each workload. This flexibility leads to significant cost savings over time.
- Vendor Lock-In Mitigation: By consciously steering clear of dependence on a sole cloud provider, multi-cloud strategies effectively reduce the risk of vendor lock-in. Consequently, organizations retain the flexibility to transition between providers or embrace a best-of-breed approach for their applications.
- Improved Performance: Multi-cloud services enable organizations to deploy workloads in geographically distributed data centers, reducing latency and improving the user experience.
- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses can meet industry-specific regulatory requirements by deploying sensitive data and applications on compliant cloud platforms while using public clouds for non-sensitive services.
Challenges of Multi-Cloud Services:
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud providers requires a sophisticated orchestration and management strategy. It can be challenging to maintain consistency across diverse platforms.
- Data Security and Compliance: Coordinating data security and compliance across various clouds demands diligent effort. Security policies, access controls, and data governance need to be standardized.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that applications can operate seamlessly across different cloud environments can be complex. Interoperability issues may arise if not addressed properly.
- Cost Monitoring: While multi-cloud can lead to cost savings, it can also lead to cost overruns if not well-managed. Careful monitoring of cloud spending is essential.
Tips for a Successful Multi-Cloud Strategy:
- Thorough Planning: Start with a well-thought-out strategy that outlines your objectives, risk tolerance, and the role each cloud service will play in your organization.
- Automation and Orchestration: Leverage automation and orchestration tools to streamline management and ensure that workloads can be moved seamlessly between clouds.
- Standardization: Standardize your cloud architecture and management practices to reduce complexity and enhance security and compliance.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor your cloud infrastructure and spending to identify areas for improvement and optimize costs.
Conclusion
Multi-cloud services have become an essential component of modern IT strategies. They offer organizations the flexibility to choose the best cloud platforms for each specific need, ensuring agility, cost savings, and improved resilience. Effective multi-cloud deployment necessitates meticulous planning, adept management, and a profound grasp of its nuances. As technology continues to evolve, embracing a multi-cloud strategy can position your organization for success in an ever-changing digital landscape.
This article thoroughly explores multi-cloud concepts, providing real-world examples. It also delves into various cloud service types and delves deep into multi-cloud infrastructure. Furthermore, we’ve tackled multi-cloud challenges and benefits while offering valuable success tips to empower your multi-cloud journey.
Adapting to evolving tech and grasping multi-cloud services are pivotal for a thriving and resilient digital future.